Acute Urine Retention: Causes and Solutions
- Vinant Bhargava

- Sep 28, 2019
- 2 min read
Problems when urinating are issues that cause both physical discomfort and worsening of the quality of life, being limiting for those who suffer from them. An example is urine retention.
Nephrologist in Delhi explains what this pathology consists of, its causes and treatment.
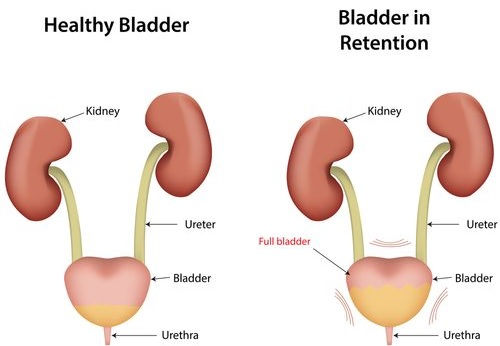
What is acute urine retention?
Acute retention of urine or AUR is the sudden inability, and in most cases, painful to urinate, even though the bladder is full. It is important to differentiate it from anuria, since in the anuria there is absence of urine production, while in retention, there is production, but no urination of it, explains the nephrologist in Noida.
In Primary Care, urinary infections are the most frequent urgencies, with urine retention being the urological urgency with the highest incidence at the hospital level.
Who can suffer acute urine retention?
Although it can manifest at any age, cases increase from 50 or 60 years, increasing as you get older.
In addition, urine retention is much more frequent in men than in women.
What are your symptoms?
According to kidney specialist in Delhi the symptoms of urine retention are the following:
Difficulty starting urination
Difficulty emptying the bladder completely
Frequent urination
Nocturia (Get up to urinate more than twice at night)
Urine flow or drip
Urine leaks
Increased abdominal pressure
Making a lot of effort to urinate
Lack of desire to urinate
Causes of acute urine retention
According to the best nephrologist in Delhi, there are several causes of urine retention, which we can divide into 4 categories, such as obstructive, pharmacological, infectious and inflammatory and neurological:
Obstructive
AUR can be associated with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia or Prostate Cancer as well as kidney or bladder stones. Other obstructions derived for example from a vaginal delivery or pelvic injuries or injuries may be the cause, explains best kidney specialist in Delhi.
Pharmacological
Anesthesia and some non-steroidal antidepressants and anti-inflammatories may promote decreased contraction of the bladder detrusor muscle.
Infectious and inflammatory
The most common in men is acute prostatitis, caused by germs such as E.coli. AUR can also be caused by sexually transmitted infections or genital herpes.
Neurological
Stroke, hydrocephalus, Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, poliomyelitis (polio), herpes zoster virus, stroke, spina bifida or spinal stenosis can be other causes due to the improper functioning of the central, autonomous and peripheral nervous systems involved in the functioning of the bladder.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of urine retention begins with the assessment of the medical history by the kidney specialist in Noida in order to know possible causes and risk factors.
Subsequently, a physical examination consisting of palpation and percussion of the abdominal area will be performed, and the doctor for kidney in Delhi may also perform a penis examination, a rectal examination and a neurological examination.
In addition, the inclusion of an analytical can be assessed.
Treatment
Most cases of AUR can be resolved in Primary Care. The first action to be carried out will be the decompression of the bladder by catheterization or catheterization (urethral or suprapubic), with the urethra being the most used.
If you have doubts about the acute retention of urine or suspect that you could suffer it, do not hesitate to contact top nephrologist in Delhi.



Comments